In recent years, Augmented Reality (AR) has transformed from a futuristic concept into a mainstream technology. With applications spanning entertainment, healthcare, retail, and education, AR enhances real-world environments with digital overlays, providing users with immersive experiences. But what exactly is AR, and how is it shaping our future? This blog explores the fundamentals, applications, and future potential of augmented reality.
What is Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality (AR) is a technology that overlays digital content—such as images, sounds, or 3D models—onto the real world through devices like smartphones, tablets, and AR glasses. Unlike Virtual Reality (VR), which creates a completely immersive digital environment, AR enhances the real world by adding interactive elements.
Brief History of AR
- 1968 – The first AR headset, the “Sword of Damocles,” was created by Ivan Sutherland.
- 1990 – The term “Augmented Reality” was coined by Tom Caudell.
- 2016 – Pokémon GO revolutionized AR gaming, bringing AR into mainstream use.
- Present Day – AR is now widely adopted in industries like retail, healthcare, and education.

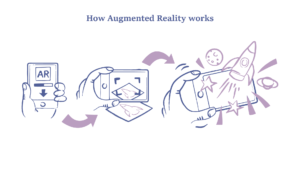
How Augmented Reality Works
Key Components of AR Technology
- Hardware – Devices such as smartphones, tablets, smart glasses, and AR headsets enable AR experiences.
- Software – AR applications use frameworks like ARKit (Apple), ARCore (Google), and Vuforia.
- Computer Vision & AI – These enable object recognition, motion tracking, and scene understanding.
- Cloud Computing – AR experiences are often powered by cloud-based platforms for real-time rendering.
Types of AR Experiences
- Marker-Based AR – Uses a camera to scan a visual marker (e.g., QR codes) to trigger digital overlays.
- Markerless AR – Uses GPS, accelerometers, and other sensors to place AR objects without a predefined marker.
- Projection-Based AR – Projects digital images onto real surfaces, allowing for interactive experiences.
- Superimposition-Based AR – Replaces or enhances parts of the real world with augmented elements (e.g., medical AR applications).
Applications of Augmented Reality
a. AR in Gaming & Entertainment
- Pokémon GO & AR Gaming – Enhances the gaming experience by integrating virtual elements into real-world environments.
- Interactive Concerts & Events – AR enables immersive live performances and fan engagement.
b. AR in Retail & E-Commerce
- Virtual Try-Ons – Brands like Sephora and IKEA use AR to let customers try on makeup or place virtual furniture in their homes.
- Augmented Shopping – Retailers use AR apps to provide additional product information when scanned.
c. AR in Education & Training
- Interactive Learning – Apps like Google Lens and AR textbooks bring subjects to life with 3D models.
- Workforce Training – AR-powered simulations train medical students, engineers, and pilots.
d. AR in Healthcare
- Surgical Assistance – AR helps surgeons visualize internal organs during operations.
- Medical Training – AR simulations enhance medical education and diagnostics.
e. AR in Real Estate & Architecture
- Virtual Property Tours – AR allows potential buyers to explore properties remotely.
- AR in Construction – Architects use AR to visualize blueprints in 3D before building.
f. AR in Automotive & Manufacturing
- Heads-Up Displays (HUDs) – Cars like BMW and Tesla use AR for navigation and driver assistance.
- Assembly Line Efficiency – AR guides workers in assembling complex machinery.
Benefits of Augmented Reality
1. Enhanced User Experience
AR makes interactions more engaging and intuitive, creating a seamless blend between the physical and digital worlds.
2. Increased Customer Engagement
Brands using AR see higher engagement rates as users are more likely to interact with AR-powered content.
3. Improved Learning & Training
AR enhances understanding through interactive and visual learning experiences, making complex concepts easier to grasp.
4. Better Decision-Making
From virtual try-ons to real-time medical visualizations, AR helps individuals make informed choices.
5. Increased Productivity
In industrial settings, AR reduces errors and streamlines workflows by providing real-time guidance and overlays.

Challenges and Limitations of AR
1. High Development Costs
Creating AR experiences requires significant investment in software, hardware, and talent.
2. Hardware Limitations
AR experiences often require high-end smartphones, AR glasses, or headsets, which may not be accessible to all users.
3. Privacy and Security Concerns
AR apps collect vast amounts of data, raising concerns about user privacy and data protection.
4. Integration Challenges
Businesses struggle to integrate AR into their existing systems effectively due to technological and financial barriers.

Future Trends in Augmented Reality
1. AR Glasses & Wearable Tech
Companies like Apple, Meta, and Google are developing advanced AR glasses to make AR more immersive and hands-free.
2. AI & AR Integration
AI-powered AR will enhance real-time object recognition, voice commands, and personalized AR experiences.
3. 5G and AR Expansion
With faster data speeds, 5G will enable more seamless and real-time AR applications.
4. AR in the Metaverse
AR will play a significant role in building the Metaverse, where digital and physical worlds merge.
5. AR for Remote Work & Collaboration
Companies are using AR for virtual meetings, interactive presentations, and remote assistance in industries like engineering and healthcare.
Conclusion
Augmented Reality is no longer a futuristic concept—it is a transformative technology that is reshaping industries and enhancing everyday experiences. From gaming and retail to healthcare and education, AR is making interactions more engaging, informative, and immersive.
As advancements in AR hardware, AI, and 5G continue, we can expect AR to become even more accessible and integrated into our daily lives. Businesses that embrace AR early will have a competitive edge in creating innovative and interactive experiences for their users.
For more informative blogs on digital marketing, visit my blog pages


Leave a Reply